Research
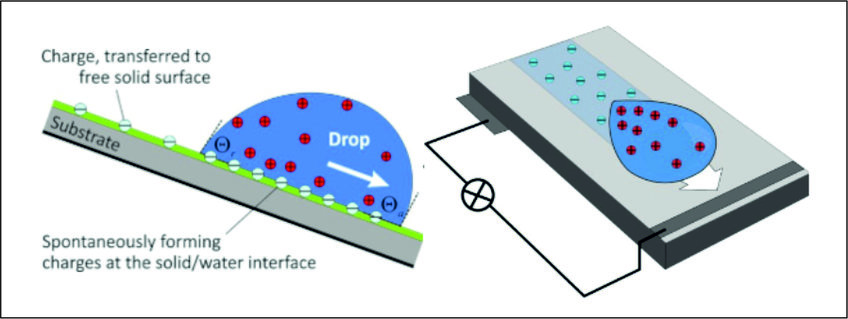
Water drops sliding over hydrophobic surfaces can lead to surface charging. In contrast to charging caused by friction between two solids, drop slide electrification is largely unexplored. Slide electrification has been consistently reported, but results are difficult to reproduce. No theory or quantitative explanation currently exists. One reason for the lack of quantitative understanding is that the deposition of charge is a non-equilibrium effect and depends essentially on microscopic processes at the contact line. Slide electrification is relevant for the friction of drops and possible corrosion due to ions deposited on surfaces. It has potential as a means of power generation.